Publications
Real-Time Multi-Person Tracking with Time-Constrained Detection
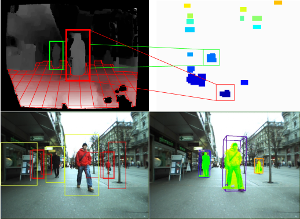
This paper presents a robust real-time multi-person tracking framework for busy street scenes. Tracking-by-detection approaches have recently been successfully applied to this task. However, their run-time is still limited by the computationally expensive object detection component. In this paper, we therefore consider the problem of making best use of an object detector with a fixed and very small time budget. The question we ask is: given a fixed time budget that allows for detector-based verification of k small regions-of-interest (ROIs) in the image, what are the best regions to attend to in order to obtain stable tracking performance? We address this problem by applying a statistical Poisson process model in order to rate the urgency by which individual ROIs should be attended to. These ROIs are initially extracted from a 3D depth-based occupancy map of the scene and are then tracked over time. This allows us to balance the system resources in order to satisfy the twin goals of detecting newly appearing objects, while maintaining the quality of existing object trajectories.
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/bmvc/MitzelSL11,
author = {Dennis Mitzel and
Patrick Sudowe and
Bastian Leibe},
title = {Real-Time Multi-Person Tracking with Time-Constrained Detection},
booktitle = {British Machine Vision Conference, {BMVC} 2011, Dundee, UK, August
29 - September 2, 2011. Proceedings},
pages = {1--11},
year = {2011},
crossref = {DBLP:conf/bmvc/2011},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.5244/C.25.104},
doi = {10.5244/C.25.104},
timestamp = {Wed, 24 Apr 2013 17:19:07 +0200},
biburl = {http://dblp.uni-trier.de/rec/bib/conf/bmvc/MitzelSL11},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, http://dblp.org}
}
Real Time Vision Based Multi-person Tracking for Mobile Robotics and Intelligent Vehicles
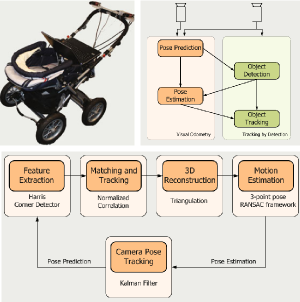
In this paper, we present a real-time vision-based multiperson tracking system working in crowded urban environments. Our approach combines stereo visual odometry estimation, HOG pedestrian detection, and multi-hypothesis tracking-by-detection to a robust tracking framework that runs on a single laptop with a CUDA-enabled graphics card. Through shifting the expensive computations to the GPU and making extensive use of scene geometry constraints we could build up a mobile system that runs with 10Hz. We experimentally demonstrate on several challenging sequences that our approach achieves competitive tracking performance.
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/icira/MitzelFSZL11,
author = {Dennis Mitzel and
Georgios Floros and
Patrick Sudowe and
Benito van der Zander and
Bastian Leibe},
title = {Real Time Vision Based Multi-person Tracking for Mobile Robotics and
Intelligent Vehicles},
booktitle = {Intelligent Robotics and Applications - 4th International Conference,
{ICIRA} 2011, Aachen, Germany, December 6-8, 2011, Proceedings, Part
{II}},
pages = {105--115},
year = {2011},
crossref = {DBLP:conf/icira/2011-2},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25489-5_11},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-642-25489-5_11},
timestamp = {Fri, 02 Dec 2011 12:36:17 +0100},
biburl = {http://dblp.uni-trier.de/rec/bib/conf/icira/MitzelFSZL11},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, http://dblp.org}
}
Efficient Use of Geometric Constraints for Sliding-Window Object Detection in Video

We systematically investigate how geometric constraints can be used for efficient sliding-window object detection. Starting with a general characterization of the space of sliding-window locations that correspond to geometrically valid object detections, we derive a general algorithm for incorporating ground plane constraints directly into the detector computation. Our approach is indifferent to the choice of detection algorithm and can be applied in a wide range of scenarios. In particular, it allows to effortlessly combine multiple different detectors and to automatically compute regions-of-interest for each of them. We demonstrate its potential in a fast CUDA implementation of the HOG detector and show that our algorithm enables a factor 2-4 speed improvement on top of all other optimizations.
Bibtex:
@InProceedings{Sudowe11ICVS,
author = {P. Sudowe and B. Leibe},
title = {{Efficient Use of Geometric Constraints for Sliding-Window Object Detection in Video}},
booktitle = {{International Conference on Computer Vision Systems (ICVS'11)}},
OPTpages = {},
year = {2011},
}
Previous Year (2010)

