Welcome

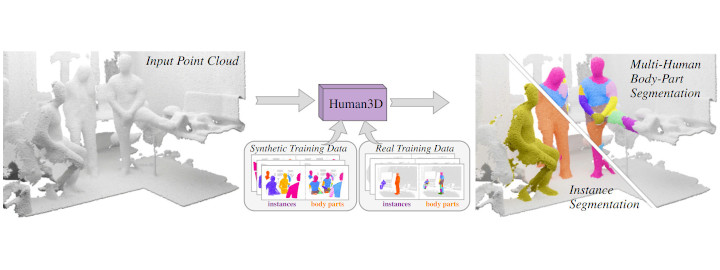

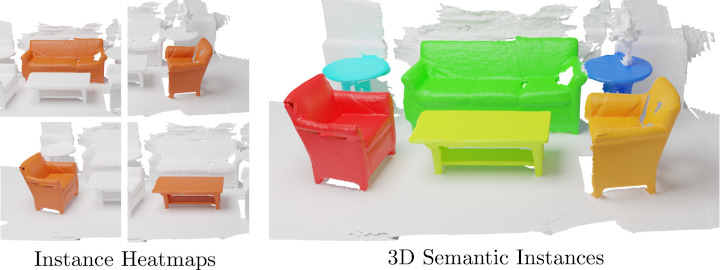

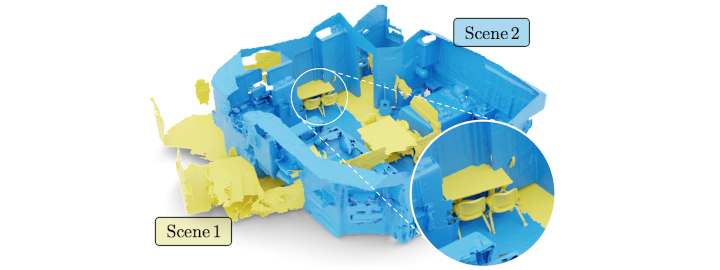


Welcome to the Computer Vision Group at RWTH Aachen University!
The Computer Vision group has been established at RWTH Aachen University in context with the Cluster of Excellence "UMIC - Ultra High-Speed Mobile Information and Communication" and is associated with the Chair Computer Sciences 8 - Computer Graphics, Computer Vision, and Multimedia. The group focuses on computer vision applications for mobile devices and robotic or automotive platforms. Our main research areas are visual object recognition, tracking, self-localization, 3D reconstruction, and in particular combinations between those topics.
We offer lectures and seminars about computer vision and machine learning.
You can browse through all our publications and the projects we are working on.
Important information for the Wintersemester 2023/2024: Unfortunately the following lectures are not offered in this semester: a) Computer Vision 2 b) Advanced Machine Learning
News
| • |
CVPR'24 We have two papers accepted at the 2024 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR):
We have two papers accepted at Workshops: |
Feb. 27, 2024 |
| • |
ICRA'24 Our Mask4Former approach has been accepted at the 2024 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA): |
Feb. 5, 2024 |
| • |
ICLR'24 Our AGILE3D approach has been accepted at the 2024 International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR): |
Jan. 27, 2024 |
| • |
GCPR'23 Two papers have been accepted for publication at the German Conference on Pattern Recognition 2023 (GCPR): |
Aug. 10, 2023 |
| • |
ICCV'23 We have two papers accepted at the 2023 International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV): |
July 16, 2023 |
| • |
CVPR'23 Our TarVIS approach has been accepted as a highlighted paper (top 2.5%) at the 2023 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR): |
March 31, 2023 |
Recent Publications
 Point-VOS: Pointing Up Video Object Segmentation IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2024 Current state-of-the-art Video Object Segmentation (VOS) methods rely on dense per-object mask annotations both during training and testing. This requires time-consuming and costly video annotation mechanisms. We propose a novel Point-VOS task with a spatio-temporally sparse point-wise annotation scheme that substantially reduces the annotation effort. We apply our annotation scheme to two large-scale video datasets with text descriptions and annotate over 19M points across 133K objects in 32K videos. Based on our annotations, we propose a new Point-VOS benchmark, and a corresponding point-based training mechanism, which we use to establish strong baseline results. We show that existing VOS methods can easily be adapted to leverage our point annotations during training, and can achieve results close to the fully-supervised performance when trained on pseudo-masks generated from these points. In addition, we show that our data can be used to improve models that connect vision and language, by evaluating it on the Video Narrative Grounding (VNG) task. We will make our code and annotations available at https://pointvos.github.io. 
|
 ControlRoom3D: Room Generation using Semantic Proxies IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2024 Manually creating 3D environments for AR/VR applications is a complex process requiring expert knowledge in 3D modeling software. Pioneering works facilitate this process by generating room meshes conditioned on textual style descriptions. Yet, many of these automatically generated 3D meshes do not adhere to typical room layouts, compromising their plausibility, e.g., by placing several beds in one bedroom. To address these challenges, we present ControlRoom3D, a novel method to generate high-quality room meshes. Central to our approach is a user-defined 3D semantic proxy room that outlines a rough room layout based on semantic bounding boxes and a textual description of the overall room style. Our key insight is that when rendered to 2D, this 3D representation provides valuable geometric and semantic information to control powerful 2D models to generate 3D consistent textures and geometry that aligns well with the proxy room. Backed up by an extensive study including quantitative metrics and qualitative user evaluations, our method generates diverse and globally plausible 3D room meshes, thus empowering users to design 3D rooms effortlessly without specialized knowledge. 
|
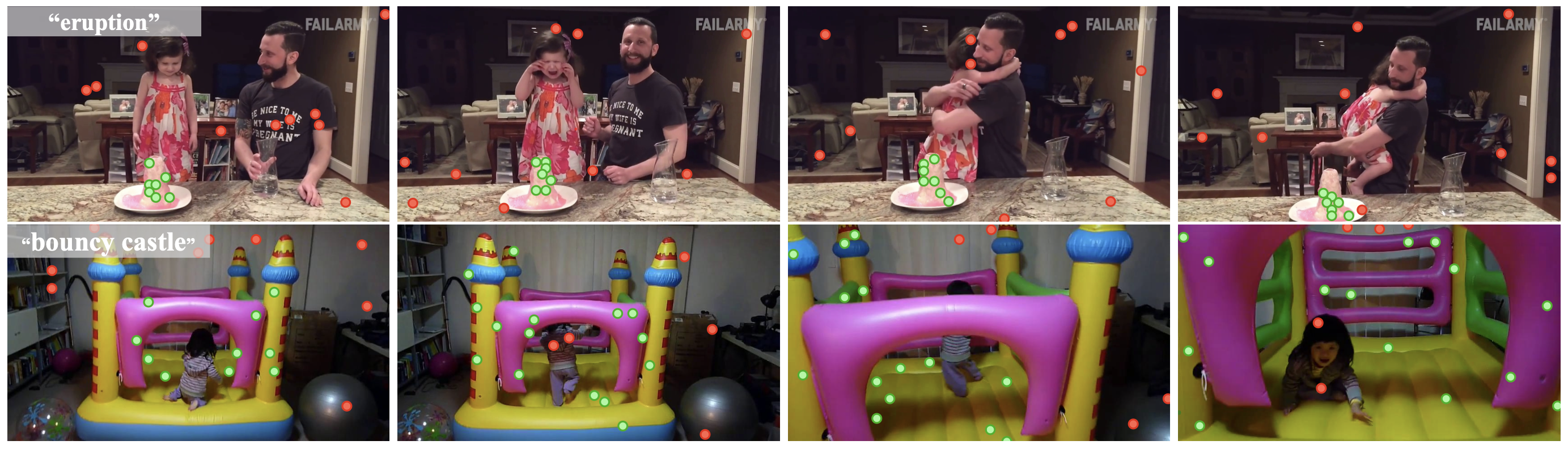
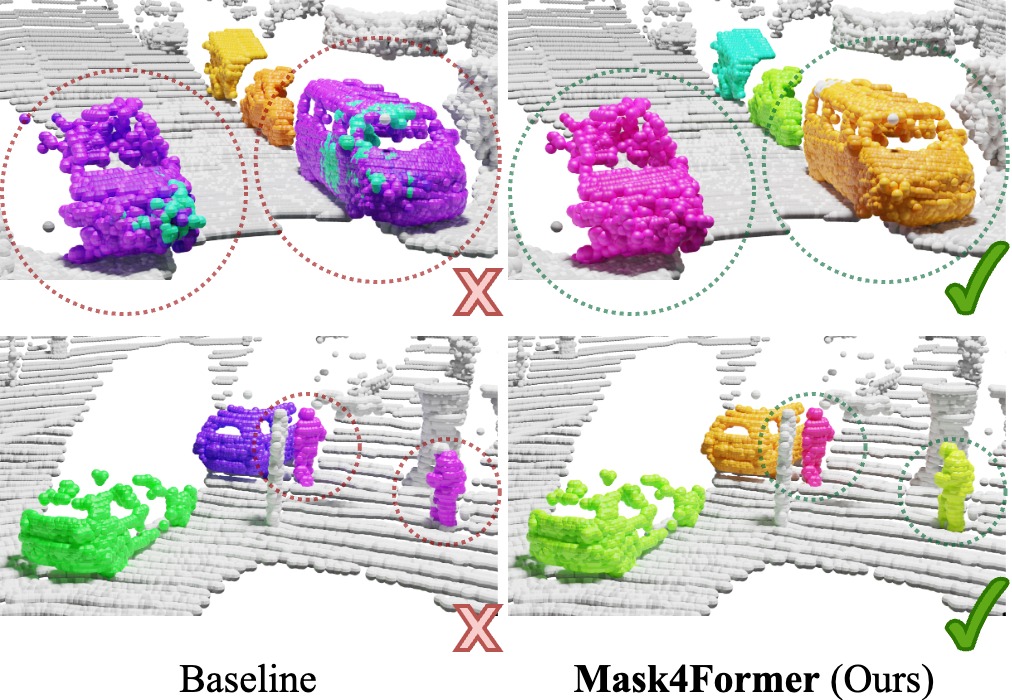 Mask4Former: Mask Transformer for 4D Panoptic Segmentation International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2024. Accurately perceiving and tracking instances over time is essential for the decision-making processes of autonomous agents interacting safely in dynamic environments. With this intention, we propose Mask4Former for the challenging task of 4D panoptic segmentation of LiDAR point clouds. Mask4Former is the first transformer-based approach unifying semantic instance segmentation and tracking of sparse and irregular sequences of 3D point clouds into a single joint model. Our model directly predicts semantic instances and their temporal associations without relying on hand-crafted non-learned association strategies such as probabilistic clustering or voting-based center prediction. Instead, Mask4Former introduces spatio-temporal instance queries that encode the semantic and geometric properties of each semantic tracklet in the sequence. In an in-depth study, we find that promoting spatially compact instance predictions is critical as spatio-temporal instance queries tend to merge multiple semantically similar instances, even if they are spatially distant. To this end, we regress 6-DOF bounding box parameters from spatio-temporal instance queries, which are used as an auxiliary task to foster spatially compact predictions. Mask4Former achieves a new state-of-the-art on the SemanticKITTI test set with a score of 68.4 LSTQ. 
|

